
The Lurking Threat of Phishing Attacks for SMBs
In an age where digital interactions have become an essential part of daily business operations, small businesses face a constant barrage of online threats. Among the most prevalent and damaging of these threats are phishing attacks. These deceptive tactics, disguised as legitimate communications, aim to steal sensitive information and wreak havoc on unsuspecting companies.
The FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) reported that in 2021, business email compromise (BEC), a sophisticated form of phishing, caused a staggering $8.6 billion in losses across the United States. With limited resources and often less robust cybersecurity frameworks compared to larger corporations, small businesses are particularly susceptible to these attacks. The consequences of a successful phishing attack can be devastating, leading to financial losses through fraudulent transactions, data breaches that expose sensitive customer information, and even reputational damage that can take years to rebuild.
To combat this critical threat, this article delves into the world of phishing, exploring its common tactics, equipping readers with the knowledge to identify fraudulent attempts, and providing actionable strategies for small businesses to protect themselves and their valuable data. We will unveil the deceptive methods employed by attackers, equip you with the tools to discern genuine communication from malicious attempts, and outline practical steps that small businesses can implement to fortify their defenses against the ever-evolving threat of phishing attacks.
Phishing Attacks: Deception Disguised as Communication

Phishing attacks operate under the cloak of deception, masquerading as legitimate communication to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information. At their core, these attempts aim to exploit human trust and capitalize on vulnerabilities in online interactions. Attackers craft emails, text messages, or phone calls that appear to originate from trusted sources, such as banks, credit card companies, or even familiar colleagues. They lure unsuspecting victims into clicking malicious links, downloading infected attachments, or revealing confidential data, like passwords or bank account details.
Phishing attacks come in various forms, each attempting to exploit different communication channels. The most prevalent method is email phishing, where fraudulent emails mimic legitimate senders, often employing spoofed email addresses or mimicking the visual identity of well-known companies. Smishing, a term derived from “SMS phishing,” involves sending deceptive text messages that urge recipients to click on malicious links or call fake customer service numbers. Similarly, vishing, short for “voice phishing,” uses phone calls to impersonate legitimate entities, attempting to trick victims into revealing sensitive information over the phone.
The prevalence and impact of phishing attacks are concerning, particularly for small businesses. According to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) 2021 report https://www.ic3.gov/, Business Email Compromise (BEC), a sophisticated form of phishing, resulted in staggering losses of $8.6 billion across the United States, with small businesses often becoming victims due to their potentially less rigorous security measures. These statistics highlight the critical need for awareness and proactive defense strategies against this ever-evolving threat.
Common Phishing Tactics Employed by Attackers

Phishing attacks thrive on deception, employing various tactics to manipulate and exploit their targets. Understanding these tactics empowers individuals to identify and avoid falling prey to these elaborate schemes.
Spoofing: Attackers often impersonate legitimate entities by manipulating sender information in emails or caller IDs during phone calls. They may use email addresses that closely resemble those of well-known companies (e.g., substituting a single character, such as “p” for “b” in “paypal.com”) or mimic the phone number format of a bank or credit card company. This creates a false sense of trust and encourages recipients to engage with the communication, potentially revealing sensitive information.
Urgency and Scarcity: Phishing attempts frequently employ tactics that create a sense of urgency or scarcity to pressure recipients into acting quickly without critical thinking. Emails might claim your account has been suspended due to suspicious activity, urging you to click a link to “verify your identity” immediately. Similarly, phone calls might warn of an impending service termination unless you “confirm your account details” over the phone. These tactics exploit the fear of missing out or facing negative consequences, leading victims to bypass their usual caution and potentially fall victim to the scam.
Pretexting: This tactic involves fabricating a scenario to gain the recipient’s trust and extract sensitive information. Attackers may pose as authority figures, such as IT support staff or company executives, claiming to investigate suspicious activity or resolve technical issues. They may also pretend to be customer service representatives offering assistance with supposed account problems. By creating a convincing scenario, they manipulate the recipient into divulging confidential data, like passwords or account numbers, under the guise of resolving a pressing issue.
Common Phishing Tactics
| Tactic | Method | Target Information |
|---|---|---|
| Spoofing | Imitate sender information (email address, phone number) of trusted entities | Email address, login credentials |
| Urgency & Scarcity | Create a sense of urgency or imminent danger | N/A (pressures immediate action) |
| Pretexting | Fabricate scenarios to gain trust and extract information | Passwords, account numbers, personal details |
By recognizing these common tactics and remaining vigilant, individuals can significantly decrease their susceptibility to phishing attacks. The next section will equip you with the knowledge to identify these deceptive attempts and protect yourself from falling victim to them.
Identifying Potential Phishing Attempts

Phishing attempts, while often sophisticated, leave behind telltale signs that can help individuals identify and avoid falling victim to their deceptive tactics. By understanding these red flags and employing a critical approach towards suspicious communication, you can significantly bolster your defenses against these malicious efforts.
Red Flags of Phishing Attempts:
- Suspicious Sender Information: Be wary of emails, calls, or messages from unfamiliar senders, especially if they claim to represent well-known organizations. Check for inconsistencies in email addresses, such as misspelled sender names, unexpected domains (e.g., “.ru” instead of “.com”), or slight variations in the actual company name.
- Generic Greetings: Phishing attempts often skip personalization and resort to generic greetings like “Dear Customer” or “Dear User”. Legitimate communication from recognized entities typically utilizes personalized salutations based on your account information.
- Urgent Language: Emails or messages that create a sense of urgency or pressure you to act immediately, like claiming your account will be suspended unless you “verify your information” right away, are strong indicators of phishing attempts. Legitimate entities rarely resort to such tactics and encourage users to take their time when addressing account-related issues.
- Grammatical Errors and Typos: Phishing attempts often originate from individuals or groups with limited language proficiency. Look for grammatical errors, typos, or awkward phrasing in the email body, which can be a red flag for deception.
- Suspicious Attachments or Links: Never click on links or open attachments embedded in emails or messages from unknown senders, or from senders whose communication raises red flags. Clicking on these links may lead to malicious websites designed to steal your information, while opening attachments can introduce malware onto your device.
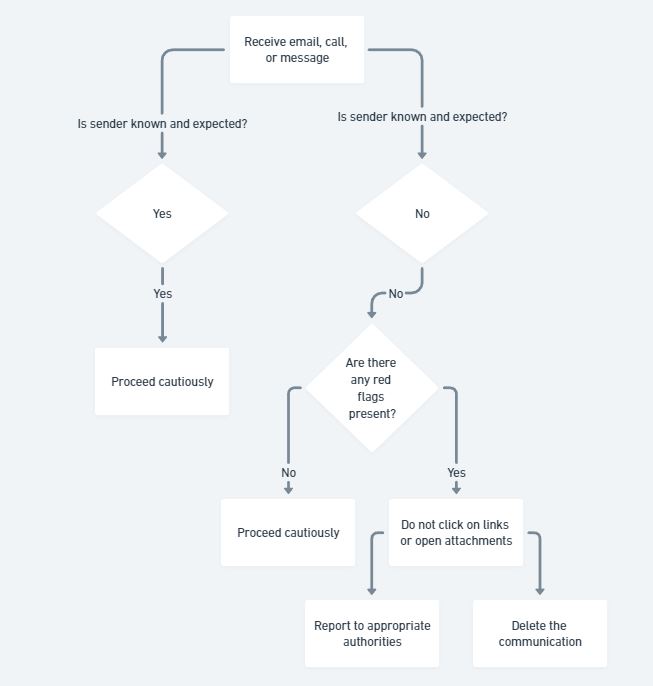
By adopting a cautious approach and utilizing the principles outlined above, individuals can significantly enhance their ability to identify and avoid falling victim to phishing attempts. The next section will delve into proactive strategies that small businesses can implement to fortify their defenses against these ever-evolving threats.
Building a Robust Defense: Preventative Measures for SMBs
While phishing attacks pose a significant threat, small businesses can implement proactive measures to bolster their defenses and significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to these deceptive tactics. By establishing robust security practices and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness among employees, businesses can significantly enhance their resilience against these ever-evolving threats.
Essential Security Best Practices:
- Implement Email Filtering and Spam Protection: Utilize robust spam filters and email security software solutions to block a significant portion of suspicious emails from reaching employee inboxes. These solutions can analyze email content, sender information, and other characteristics to identify and filter out potential phishing attempts.
- Enforce Strong Password Policies: Encourage employees to create strong and unique passwords for all business accounts. These passwords should be a minimum length, contain a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, and avoid easily guessable information like personal details or birthdays. Additionally, consider implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible, adding an extra layer of security beyond passwords.
Employee Education and Empowerment:
- Regular Employee Training: Conduct regular cybersecurity awareness training sessions for employees. These sessions should educate them on various phishing tactics, the red flags to watch out for, and safe practices to adopt when handling emails, calls, and messages.
- Phishing Simulations: Simulate phishing attacks in a controlled environment to assess employee awareness and preparedness. By experiencing these simulations, employees can develop their skills in identifying and reporting suspicious communication attempts.
- Establish Transparent Reporting Protocols: Define precise and structured protocols for employees to notify the appropriate parties about potential phishing incidents. This process may include sending the questionable email to the IT department, marking it in the email system, or informing a specific person. Such immediate and effective notification facilitates the quick examination and resolution of possible security risks.
By implementing these preventative measures and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness within the organization, small businesses can significantly strengthen their defenses against phishing attacks and safeguard their valuable data and resources.
Vigilance in the Face of Deception
Phishing attacks, constantly evolving and employing ever-more sophisticated tactics, remain a significant threat to the digital security of individuals and businesses alike. The potential consequences, ranging from financial losses to reputational damage, necessitate a proactive approach to combat these deceptive attempts. By equipping themselves with the knowledge to identify red flags and implementing robust security best practices, small businesses can significantly bolster their defenses. Additionally, fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness among employees empowers them to play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information and mitigating the impact of these malicious efforts. Remember, vigilance and proactive measures remain the most effective weapons in the ongoing fight against phishing attacks.
Don’t stop at identifying phishing attempts! Proactive measures are essential for safeguarding your organization from ever-evolving cyber threats. Learn how to conduct a comprehensive security gap assessment to fortify your defenses and minimize your risk in our in-depth guide: Best Practices for Conducting a Security Gap Assessment.
Categorized in:
Comments