
The contemporary digital environment has woven itself into the fabric of our daily lives. From social media platforms teeming with personal data to online banking portals safeguarding financial assets, we entrust a vast array of sensitive information to a multitude of online accounts. Access to these accounts is secured by passwords, acting as the digital gatekeepers protecting our privacy and security. However, the escalating prevalence of cyberattacks casts a long shadow over this digital landscape. In 2023 alone, a staggering 81% of businesses reported experiencing at least one cyberattack, according to a report by IBM (https://www.ibm.com/reports/threat-intelligence).
The consequences of weak password management can be catastrophic. Data breaches, where sensitive information is exposed to unauthorized individuals, can have a devastating ripple effect. In 2022, the average cost of a data breach reached a record high of $4.24 million globally, as reported by the Ponemon Institute (https://www.businessinsurance.com/article/20230725/NEWS06/912358845/Cost-of-data-breaches-reaches-all-time-high-IBM,-Ponemon). Identity theft, where criminals misuse stolen personal information for fraudulent purposes, can result in significant financial losses and damage an individual’s creditworthiness. The ease with which weak passwords can be compromised underscores the critical need for robust password management strategies in the face of an ever-evolving cyber threat landscape.
Why Strong Passwords Matter

In the intricate web of online accounts that underpins our modern lives, passwords function as the initial line of defense against unauthorized access. These digital sentinels stand guard, safeguarding a treasure trove of sensitive information, from financial records and personal documents to communication logs and professional credentials. Yet, traditional password practices often fall short in the face of increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks.
While simple passwords like birthdates or favorite words may have sufficed in the past, the evolution of cybercrime necessitates a more robust approach. Brute-force attacks, a relentless method that systematically tries every possible password combination, can swiftly crack weak passwords. Imagine a determined thief trying every key on a keyring until they find the one that unlocks the door a brute force attack operates on a similar principle, but with an automated and exponentially faster pace.
Furthermore, password-cracking techniques like dictionary attacks exploit commonly used words and phrases. These attacks leverage vast databases of frequently used terms to guess passwords, akin to a criminal with a master list of stolen keys attempting to match them to specific locks. The sheer volume of attempts associated with these techniques highlights the vulnerability of weak passwords.
Herein lies the paramount importance of password strength. A strong password, meticulously crafted with a combination of length, complexity, and uniqueness, presents a formidable obstacle to cybercriminals. Length, measured in characters, significantly increases the number of possible combinations, making brute-force attacks computationally expensive and time-consuming. Complexity, achieved by incorporating a diverse mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, further frustrates automated cracking attempts. Finally, uniqueness, ensuring each password is distinct for every account, minimizes the potential damage from a single breach. By prioritizing strong passwords, we can significantly enhance the security posture of our online accounts and thwart a wide range of cyberattacks, safeguarding our valuable data and digital identities.
Additional Resources:
For a deeper understanding of cybersecurity assessments, consider exploring resources offered by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) on cybersecurity risk management: https://www.nist.gov/cybersecurity.
Characteristics of a Strong Password

Crafting a strong password is akin to constructing a formidable digital fortress. Three key characteristics, length, complexity, and uniqueness form the cornerstones of this defensive structure.
Length serves as the initial barrier against unauthorized access. Aim for a minimum password length of 12-16 characters. The more characters your password comprises, the exponentially more time-consuming it becomes for attackers to crack using brute-force methods. Imagine a determined burglar attempting to break into a vault – a longer, more complex combination lock significantly increases the time and effort required for a successful breach. Similarly, a longer password exponentially expands the number of possible combinations, making it computationally expensive for attackers to guess through every option.
Complexity adds another layer of defense by incorporating a diverse mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. This heterogeneity functions like a multifaceted security system, where each element presents a distinct obstacle. A password consisting solely of lowercase letters offers a single point of entry for attackers. Conversely, a password that blends uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols presents multiple hurdles, significantly reducing the effectiveness of automated cracking attempts that rely on common character sets.
Finally, uniqueness is paramount. Refuse the urge to employ the same passwords for various accounts. A data breach on a single platform can have a domino effect, compromising all your other accounts if they share the same password. Consider each account a separate vault, each requiring its own unique and secure key. By employing distinct passwords, you minimize the potential damage from a single breach, ensuring that a compromised login for one platform doesn’t unlock the doors to all your other online assets.
By prioritizing these three characteristics, you can significantly strengthen your passwords and bolster the security of your online presence. Remember, a strong password is a cornerstone of effective cybersecurity, safeguarding your sensitive data and digital identity from a constantly evolving threat landscape.
Common Password Mistakes to Avoid

While the desire for convenience can lead users astray, certain password practices inadvertently create vulnerabilities that cybercriminals readily exploit. Here, we explore some common password mistakes to steer clear of:
- Personal Information: Birthdays, pet names, addresses, or phone numbers may seem like harmless choices, but they hold the key to unlocking your digital identity. Savvy attackers can often glean such information through social media profiles or public records, rendering these passwords easily guessable.
- Dictionary Words: Even misspelled variations of dictionary words are prime targets for automated attacks. These tools exploit vast databases of commonly used terms, making password combinations predictable and vulnerable.
- Simple Keyboard Patterns: Sequential patterns like “123456” or repetitive characters (e.g., “aaaaaa”) offer minimal security and can be cracked with minimal effort. Imagine a combination lock with only a few numbers – such a simple mechanism provides scant protection.
The dangers of password reuse are particularly noteworthy. Utilizing identical passwords across multiple accounts initiates a cascading effect. If a single account is compromised due to a weak password, all your other accounts employing that same password become vulnerable, potentially leading to a cascading data breach. By avoiding these common pitfalls and adopting robust password practices, you can significantly enhance your online security posture.
Creating Strong and Memorable Passwords

Crafting strong passwords can seem like a daunting task, especially when faced with the challenge of memorizing a complex string of characters. However, there are practical strategies to create passwords that are both robust and readily recalled.
One effective approach involves utilizing passphrases. Instead of a single word, consider using a string of unrelated words separated by spaces or symbols. This approach leverages the inherent strength of length and complexity while enhancing memorability. For instance, the phrase “RedBicycleJumpsOverMoonbeam” creates a strong password that is considerably easier to remember than a random collection of letters, numbers, and symbols.
Here are some techniques to create memorable passphrases:
- Mnemonic Phrase: Construct a memorable sentence or phrase that is easy to recall. You can then extract the first letter of each word to form your password. Imagine a sentence like “Every Good Boy Deserves Fudge” – the first letters create the password “EGBDF.” This method allows you to leverage a familiar phrase as the foundation for a complex password.
- First Letter Method: Choose a quote, song lyric, or personal motto that holds significance for you. Extract the first letter of each word, incorporating numbers and symbols to further enhance complexity. For example, the quote “The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog” could be transformed into a password like “Tqbfj0v0tld” – a strong and memorable choice based on a familiar saying.
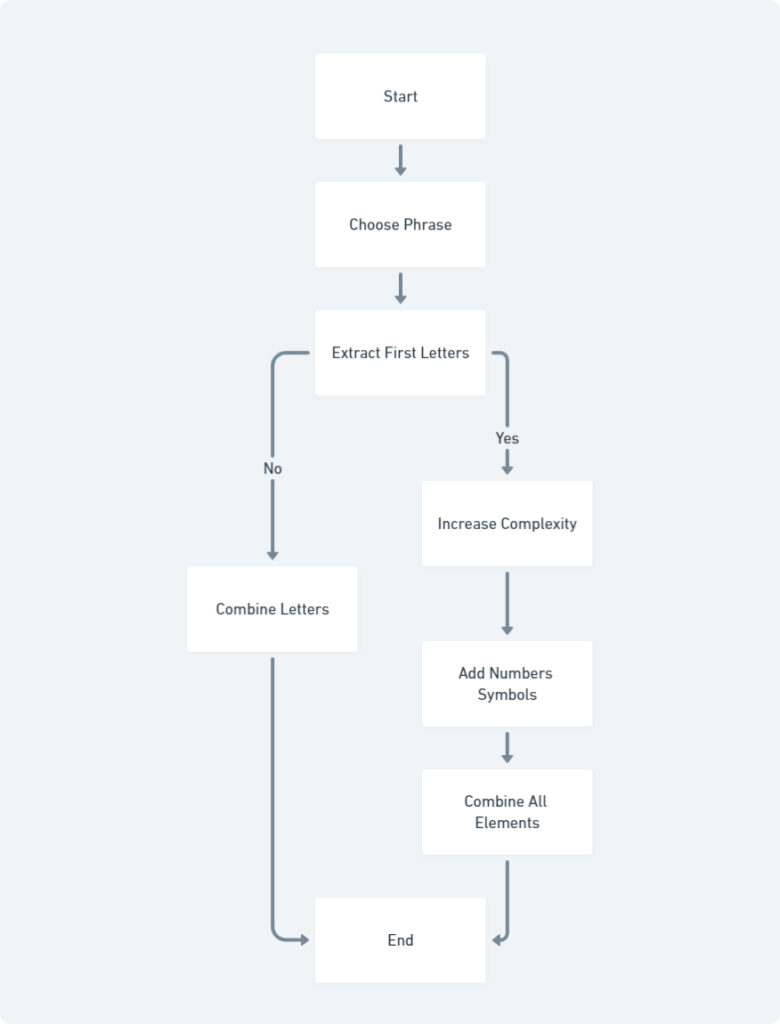
By employing these techniques, you can strike a balance between password strength and memorability. Remember, a strong password is the first line of defense against unauthorized access to your online accounts. By investing time and creativity into crafting robust and memorable passwords, you can significantly bolster your online security posture.
Password Management Tools

Navigating the digital landscape often necessitates juggling a multitude of accounts, each requiring its own unique and robust password. Remembering a plethora of complex passwords can be a formidable challenge. Thankfully, password management tools offer a secure solution to this dilemma.
These applications function as digital vaults, securely storing your passwords in an encrypted format. Imagine a virtual safe, meticulously safeguarding your passwords behind a single, strong master password. This master password acts as the primary key, granting access to the entire collection of passwords within the vault. Password managers provide a multitude of advantages:
- Automatic Password Generation: They can generate strong, unique passwords for each of your accounts, eliminating the need for manual creation and the associated risk of weak, repetitive passwords.
- Secure Storage: Encrypted storage ensures your passwords are not exposed to unauthorized individuals, even if a hacker gains access to your device.
- Autofill Functionality: Many password managers offer autofill functionality, streamlining the login process across various websites and applications. This not only saves time but also reduces the risk of mistyping your password and inadvertently locking yourself out of your accounts.
By leveraging password management tools, you can significantly enhance your online security posture. These tools alleviate the burden of memorizing complex passwords while ensuring their safe and secure storage. This allows you to focus on creating strong, unique master passwords, the key that unlocks your digital vault and safeguards your online identity.
Additional Security Practices: Bolstering Online Defenses

While strong passwords form the cornerstone of online security, a layered approach is paramount in today’s ever-evolving cyber threat landscape. Here are some additional practices to fortify your digital defenses:
- Embrace Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): When available, enable 2FA for your online accounts. This additional verification step transcends the reliance solely on your password. With 2FA, a secondary code, often sent via SMS or generated by an authenticator app, is required to gain access. This additional hurdle significantly hinders unauthorized attempts, even if a cybercriminal manages to obtain your password.
- Beware of Phishing Scams: Phishing emails or websites designed to mimic legitimate entities can trick you into revealing sensitive information, including passwords. Maintain a healthy dose of skepticism towards unsolicited emails, and avoid entering passwords on suspicious websites. Legitimate companies will not request your password via email – if in doubt, log in directly to the official website instead of clicking on links within emails.
- Prioritize Software Updates: Regularly updating software and applications on your devices addresses known security vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals capitalize on these weaknesses to attain unauthorized entry into systems. By promptly installing security patches and updates, you significantly reduce the potential attack surface and bolster your online security posture.
By implementing these additional security practices alongside robust password management, you can create a multi-layered defense against cyber threats. Remember, vigilance and a proactive approach are crucial in safeguarding your online identity and sensitive data in a world where cyberattacks are constantly evolving.
Your Digital Armor

Strong password management serves as the cornerstone of online security. By implementing the best practices outlined in this article – crafting robust passwords, leveraging secure storage solutions, and adopting additional security measures – you can significantly enhance your digital defense posture. Remember, a proactive approach to password hygiene is paramount in safeguarding your sensitive information and maintaining control over your online identity. Navigate the digital landscape with confidence, knowing you’ve erected a formidable digital fortress against cyber threats.
- For a deeper dive into digital identity guidelines, explore the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) publication: Digital Identity Guidelines: https://pages.nist.gov/800-63-3/
- Enhance your password security knowledge with tips from the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA): Password Safety Tips: https://www.cisa.gov/sites/default/files/publications/NCSAM_CreatingPasswords_2020.pdf
For further insights into strengthening cybersecurity culture and establishing communication channels within teams, read the article ‘Building a Strong Cybersecurity Culture: Going Beyond Training.’ This article provides strategies and free resources for enhancing security in business environments. Click here to access the article.
Categorized in:
Comments