
Ransomware Spikes in 2023 - IBM X-Force Report
The contemporary business landscape is undeniably digitized, with vast swathes of sensitive information stored and transmitted electronically. This interconnected environment has unfortunately become a breeding ground for cybercriminals. The IBM Security X-Force Threat Intelligence Index 2023 reported a staggering 170% increase in ransomware attacks alone, highlighting the escalating severity of the cyber threat.
In this ever-evolving threat landscape, robust cybersecurity practices are no longer a luxury, but a fundamental necessity for businesses of all sizes. A cornerstone of this defense lies in cultivating a robust security culture – a shared understanding and commitment to cybersecurity within an organization. This culture fosters a proactive environment where employees actively participate in safeguarding sensitive data and mitigating cyber risks. By implementing strategies that encourage employee engagement, businesses can significantly bolster their overall cybersecurity posture and minimize the potential for costly breaches.
The Importance of a Security Culture

A security culture transcends mere technical controls; it represents the collective beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors within an organization regarding cybersecurity. It thrives on three core principles: shared responsibility, continuous learning, and open communication. Shared responsibility acknowledges that cybersecurity is not solely an IT department concern, but a collective effort requiring vigilance from every employee. Continuous learning ensures employees stay abreast of evolving cyber threats by incorporating regular security awareness training into the organizational workflow. Open communication fosters a safe space for employees to report suspicious activity or raise security concerns without fear of reprisal.
By cultivating a security culture, organizations empower their workforce to become the first line of defense against cyberattacks. A vigilant and informed employee base is significantly less susceptible to social engineering tactics often employed by cybercriminals. Phishing emails, for instance, rely on an element of surprise or confusion to trick recipients into clicking malicious links or divulging sensitive information. Employees equipped with cybersecurity awareness training are better prepared to identify these red flags and report them appropriately, hindering the attacker’s progress.
Further emphasizing the financial implications of a weak security culture, a 2023 study by IBM’s X-Force Incident Response and Intelligence Services team found that organizations with a low level of security maturity experienced an average total cost of a data breach of $4.35 million, a significant 10% increase compared to those with a more mature security culture. This data underscores the critical role a security culture plays in mitigating not only security risks, but also the substantial financial repercussions associated with cyberattacks. Businesses of all sizes, from those seeking information on “cybersecurity for small business” to established enterprises conducting a “cybersecurity assessment” or “security gap analysis,” can significantly benefit from fostering a robust security culture within their organization.
Resources:
- IBM Security X-Force Threat Intelligence Index 2023: https://www.ibm.com/reports/threat-intelligence
Challenges and Considerations

While the benefits of a robust security culture are undeniable, fostering one presents several hurdles. Apathy towards cybersecurity can be a significant obstacle. Employees burdened with daily tasks may not readily perceive the immediate relevance of security protocols. This lack of understanding can lead to a “check-the-box” mentality towards security awareness training, hindering its effectiveness.
Another key challenge lies in inadequate training. Generic, one-size-fits-all security programs often fail to resonate with employees. For a cybersecurity awareness program to be truly impactful, it should be tailored to the specific industry and employee demographics within the organization. For instance, a financial services firm would require training that addresses financial fraud attempts, while a healthcare organization might prioritize awareness of patient data privacy regulations.
Furthermore, a culture of fear can impede open communication, a cornerstone of a strong security culture. Employees may hesitate to report suspicious activity or security incidents for fear of being reprimanded or blamed. Fostering an environment of psychological safety, where employees feel empowered to report concerns without repercussions, is crucial.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-pronged approach. Engaging security awareness programs that utilize real-world scenarios relevant to the specific industry can spark employee interest. Additionally, establishing clear reporting procedures and a culture of open communication are essential to encourage employees to become active participants in safeguarding the organization.
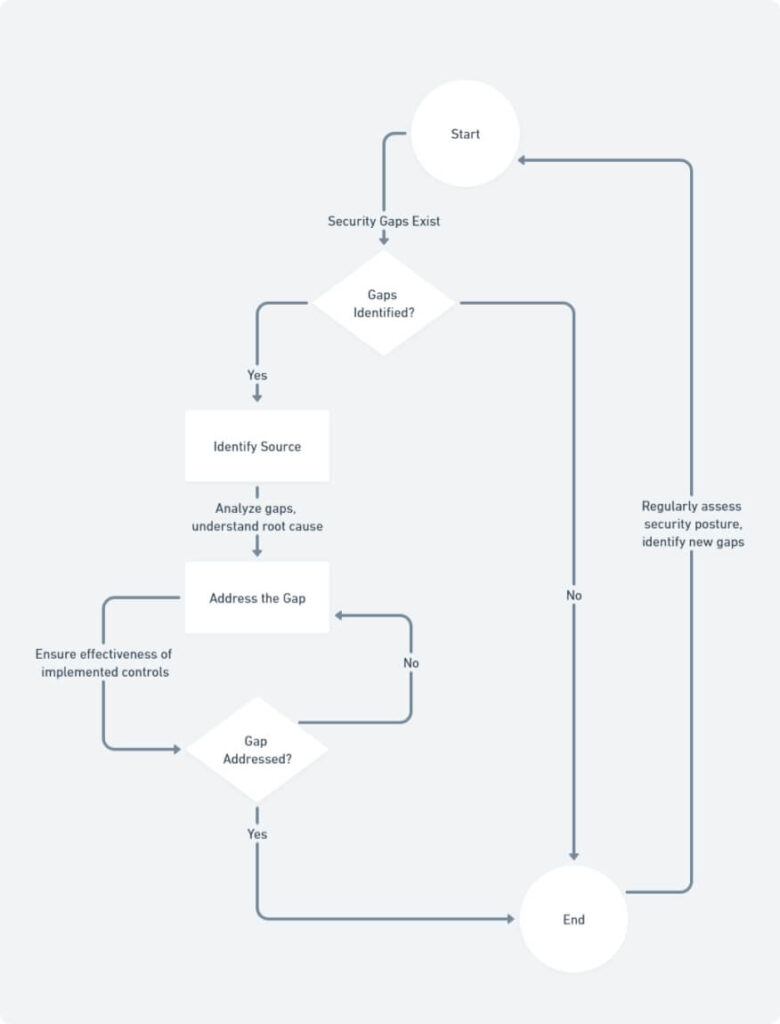
Building Your Security Culture
Cultivating a robust security culture is an ongoing process that requires a strategic and collaborative approach. Here are some key steps to foster a security-conscious work environment:

Leadership Buy-in
Executive leadership plays a pivotal role in establishing cybersecurity as a core organizational value. When leaders actively champion security initiatives, it sends a powerful message that security is not an afterthought, but a critical aspect of everyday operations. Leaders can demonstrate their commitment by:
- Allocating resources for security awareness training
- Participating in security drills
- Openly communicating the importance of cybersecurity to the entire organization
Comprehensive Training
Effective security awareness training equips employees with the knowledge and skills to identify and mitigate cyber threats. Gone are the days of dry, text-heavy lectures. Engaging, ongoing training programs that cater to different learning styles are crucial. Here’s how to make training more effective:
- Interactive Modules: Utilize interactive quizzes, drag-and-drop activities, or scenario-based challenges to keep employees engaged.
- Video Simulations: Simulate real-world phishing attempts or social engineering tactics to help employees recognize red flags.
Real-World Scenarios: Tailor training content to the specific industry and threats relevant to the organization.
Incorporating Phishing Simulations and Gamified Learning
Phishing simulations replicate real-world phishing attempts, allowing employees to test their ability to recognize and avoid them. These simulations provide valuable learning experiences and help employees develop a healthy skepticism towards suspicious emails. Additionally, gamified learning elements, such as points, badges, and leaderboards, can inject a fun and competitive spirit into security training, further boosting employee engagement.
Clear Policies and Procedures
Well-defined security policies provide a clear framework for employee behavior when handling sensitive data and utilizing company technology. These policies should encompass areas such as:
- Password management practices (e.g., complexity requirements, changing passwords regularly)
- Data encryption protocols (e.g., encrypting sensitive data on portable devices)
- Acceptable use of technology (e.g., personal device usage, social media guidelines)
- Reporting procedures for suspicious activity (e.g., dedicated hotline, email address)
By establishing clear expectations, organizations empower employees to make informed decisions and minimize security risks.
Open Communication Channels
Building an environment of trust is paramount. Employees must feel comfortable reporting suspicious activity or security incidents without fear of reprimand or blame. This necessitates establishing open communication channels, such as:
- Anonymous reporting hotlines
- Dedicated security awareness email addresses
By actively listening to employee concerns and fostering a culture of open dialogue, organizations can address potential security issues before they escalate into major breaches.
These steps provide a solid foundation for building a strong security culture. Remember, security awareness is an ongoing journey, not a one-time destination. Implementing these strategies and continuously monitoring their effectiveness will empower your workforce to become a vital line of defense against cyber threats.
Security Awareness Training Content & Benefits

| Security Awareness Training Content | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Phishing Awareness | Teaches employees to identify and avoid phishing emails, a common tactic used by cybercriminals to steal credentials or sensitive data. |
| Password Hygiene | Educates employees on creating strong, unique passwords and the importance of changing them regularly. |
| Data Security | Informs employees about data security best practices, such as data classification, encryption, and responsible data handling. |
| Social Engineering Awareness | Equips employees to recognize and resist social engineering tactics used to manipulate them into divulging sensitive information. |
| Malware Awareness | Explains the different types of malware and how to avoid them, including viruses, ransomware, and spyware. |
| Security Patch Management | Emphasizes the importance of installing security patches promptly to address vulnerabilities in software and operating systems. |
| Incident Reporting | Provides clear procedures for employees to report suspicious activity or security incidents to the appropriate authorities. |
By incorporating a variety of security awareness training content that addresses these critical areas, organizations can significantly enhance their overall cybersecurity posture.
Encouraging Employee Participation

Building a strong security culture hinges not only on education and awareness but also on active employee participation. Employees are the human firewall of an organization, and their vigilance is crucial in thwarting cyberattacks. Here are various strategies to motivate employees to become active partners in cybersecurity:
Recognition and Rewards
Positive reinforcement through a well-designed reward system can incentivize employees to consistently demonstrate secure behavior. This does not necessarily entail a substantial financial investment. Public recognition through acknowledgements in company newsletters or team meetings can be highly motivating. Additionally, awarding small tokens of appreciation, such as gift cards or extra time off, can further bolster participation. The key is to ensure the rewards are relevant and celebrate achievements that directly contribute to a more secure work environment.
Empowerment
Empowering employees to make informed security decisions fosters a sense of ownership and accountability. Equipping them with clear security policies and procedures is essential. However, organizations can take this a step further by granting employees the autonomy to implement these procedures within their specific roles. For instance, enabling employees to set strong passwords for their work accounts and requiring them to change them regularly demonstrates trust and empowers them to take ownership of their cybersecurity hygiene.
This sense of ownership fosters a proactive environment where employees go beyond simply following the rules and become invested in identifying and reporting potential security risks. When employees feel empowered to make security decisions, they are more likely to be vigilant and take initiative to safeguard sensitive data.
Security Champions
Designating security champions within departments can act as a powerful force in driving employee engagement. Security champions are knowledgeable peers who can serve as internal educators, reinforcing security best practices and creating a culture of open communication. These champions can be nominated by their peers or management and should possess a strong understanding of the organization’s security policies and procedures.
Security champions can play a critical role in dispelling common misconceptions about cybersecurity and simplifying complex security concepts for their colleagues. Furthermore, they can create a safe space for open dialogue, encouraging employees to voice concerns and ask questions without fear of judgment. This peer-to-peer approach can be particularly effective in fostering a sense of community and shared responsibility for cybersecurity within the organization.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can move beyond a culture of compliance and cultivate a culture of security ownership. Employees who feel valued, empowered, and recognized for their security contributions are more likely to become active participants in safeguarding the organization’s data and mitigating cyber threats.
Cultivating a robust security culture is no longer optional – it’s a necessity for businesses of all sizes navigating today’s ever-evolving cyber threat landscape. By prioritizing leadership buy-in, implementing engaging security awareness programs, and establishing clear communication channels, organizations can empower employees to become active participants in cybersecurity. Recognizing and rewarding secure behavior further incentivizes participation. Ultimately, fostering a culture of security ownership strengthens an organization’s overall cybersecurity posture and minimizes the risk of costly data breaches. Investing in a strong security culture is an investment in the long-term success and resilience of your business.
Further Reading: Strengthening Your Password Security
For more in-depth insights into bolstering your online security through effective password management, consider reading our companion article: “Securing Your Passwords: Best Practices for Strong Password Management.” This comprehensive guide delves into the importance of strong passwords, common pitfalls to avoid, and practical strategies for crafting and managing robust passwords.
Categorized in:
Comments