
The once-nebulous concept of cybersecurity has become a critical concern for small businesses in the modern era. No longer the exclusive domain of large corporations, cyberattacks are increasingly targeting smaller businesses due to their perceived vulnerability. A 2023 report by Verizon’s Data Breach Investigations Report found that 43% of all cyberattacks targeted small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). The financial repercussions of such attacks can be devastating. The same report indicates that the average cost of a data breach for an SMB is a staggering $82,280, a figure that can cripple a small business.
Beyond the immediate financial losses, cyberattacks can inflict lasting reputational damage. A successful attack can expose sensitive customer data, erode trust, and hinder a small business’s ability to attract new clients. In today’s hyper-connected world, a data breach can quickly become a public relations nightmare, potentially leading to lost business and a tarnished brand image.
The good news is that small businesses don’t have to be passive targets. By proactively leveraging cybersecurity measures, they can significantly enhance their protection and mitigate the risks associated with cyberattacks. This article will equip you with the knowledge and guidance to develop a robust cybersecurity strategy, safeguarding your business and fostering continued growth.
The Cybersecurity Landscape for Small Businesses

Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. At its core, cybersecurity is built upon three fundamental principles:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive information.
- Integrity: Guaranteeing the accuracy and completeness of data and systems.
- Availability: Maintaining the accessibility of critical systems and information whenever needed.
While large corporations have long been a target for cyberattacks, small businesses are increasingly finding themselves on the radar of cybercriminals. This vulnerability stems from several factors. Small businesses may lack the robust cybersecurity defenses often employed by larger companies, making them easier targets for attackers. Additionally, small businesses often hold valuable data that cybercriminals seek to exploit, such as customer information, financial records and intellectual property.
| Attack Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Phishing | Deceptive emails or messages designed to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links. |
| Malware | Malicious software that can infect computer systems and steal data, disrupt operations, or render systems unusable. |
| Ransomware | A specific type of malware that encrypts a victim's data, essentially holding it hostage until a ransom is paid. |
These are just a few examples of the many cyber threats faced by small businesses. Understanding the cybersecurity landscape and the tactics employed by cybercriminals is the first step towards developing a robust defense strategy.
Why Small Businesses Need a Cybersecurity Strategy

For small businesses, the consequences of a cyberattack can be catastrophic. While the financial losses can be significant, the true cost extends far beyond immediate monetary damages. The 2023 IBM Security X-Force Threat Intelligence Index found that the average total cost of a data breach for a small business is a staggering $4.24 million. This figure encompasses not just financial compensation for stolen data but also factors like legal fees, forensic investigations, and lost revenue due to operational disruptions.
Beyond the immediate financial burden, cyberattacks can severely disrupt a small business’s day-to-day operations. A successful attack can disable critical systems, hindering communication, data processing, and even customer service capabilities. This downtime can translate into lost productivity, missed deadlines, and ultimately, lost revenue.
The reputational damage inflicted by a cyberattack can be equally devastating for a small business. News of a data breach can erode customer trust, leading to a decline in sales and a tarnished brand image. Rebuilding trust with customers takes time and significant effort, highlighting the importance of proactive cybersecurity measures.
A strong cybersecurity strategy serves as a critical line of defense for small businesses navigating the ever-evolving threat landscape. Here’s how a well-defined strategy can benefit your business:
- Mitigate Cyber Risks: By proactively identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, a cybersecurity strategy can significantly reduce the likelihood of a successful cyberattack. This includes conducting regular cybersecurity risk assessments to identify potential weaknesses in your systems and implementing appropriate safeguards.
- Protect Sensitive Data: Customer information, financial records, and intellectual property are all valuable assets for small businesses. A robust cybersecurity strategy safeguards this sensitive data through measures like encryption, access controls, and data backups.
- Maintain Business Continuity: Cyberattacks can cripple a small business’s operations. A cybersecurity strategy that incorporates incident response planning and disaster recovery procedures ensures that your business can quickly recover from an attack and minimize downtime.
- Build Customer Trust: In today’s data-driven world, customers are increasingly concerned about the security of their personal information. By demonstrating a commitment to cybersecurity, small businesses can build trust with their customers, fostering stronger relationships and loyalty.
Building a Cybersecurity Strategy for Your Small Business

Just as a blueprint guides the construction of a sturdy building, a cybersecurity framework provides a structured approach to safeguarding your small business’s digital assets. These frameworks outline a set of best practices and recommendations, enabling small businesses to build a robust cybersecurity posture without getting overwhelmed by the technical complexities.
- Identify: Catalog your critical assets and identify potential threats.
- Protect: Implement safeguards to mitigate identified risks.
- Detect: Establish mechanisms to identify and respond to cyberattacks.
- Respond: Develop a plan for containing and recovering from an attack.
- Recover: Restore your systems and data following a cyberattack.
The beauty of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework lies in its flexibility. Small businesses can tailor the framework to their specific needs and resources.
Here’s a step-by-step approach to developing a cybersecurity strategy for your small business:
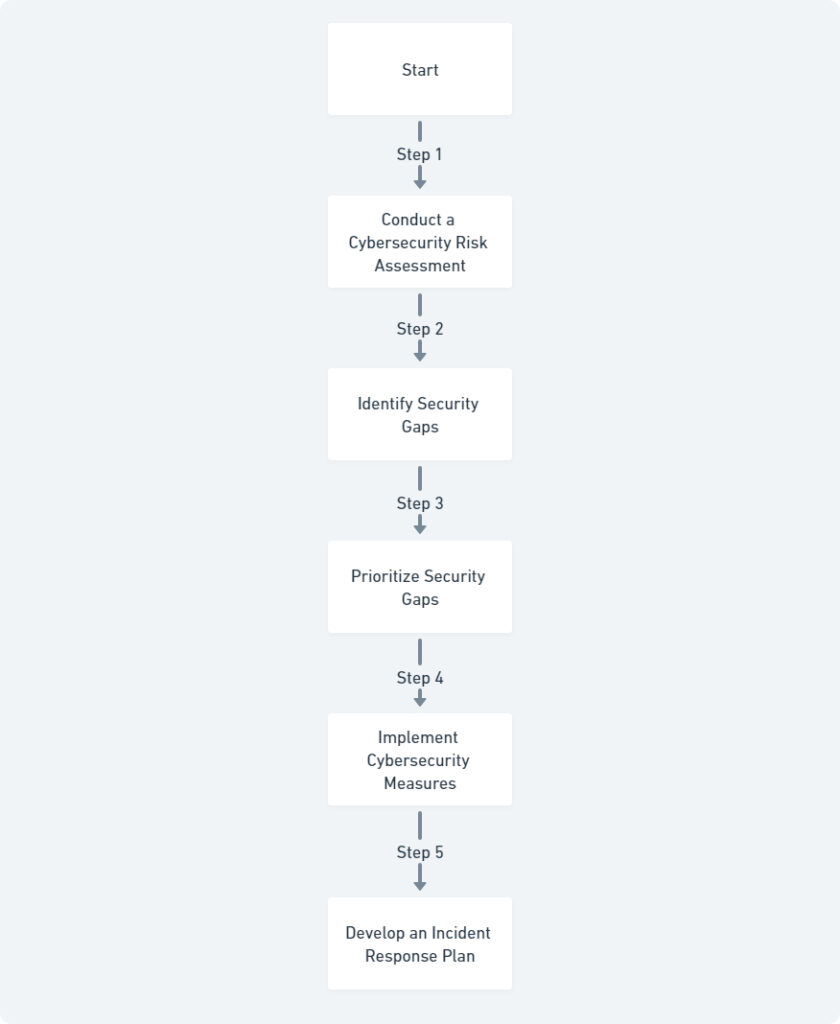
1. Conduct a Cybersecurity Risk Assessment
A cybersecurity risk assessment is a systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing potential threats to your IT infrastructure and data. This assessment serves as the foundation for your cybersecurity strategy, highlighting areas that require the most attention.
Several free or low-cost online tools can assist you in conducting a basic risk assessment. The Small Business Administration (SBA) website offers a helpful guide on “How to Conduct a Cybersecurity Risk Assessment for Your Business“.
2. Identify and Prioritize Security Gaps
Based on your risk assessment, pinpoint weaknesses in your cybersecurity posture. Prioritize these security gaps according to the severity of the potential threats and the value of the assets at risk.
3. Implement Cybersecurity Measures
There’s no single silver bullet for cybersecurity. A layered defense approach incorporating several essential measures is most effective for small businesses. Consider the following:
- Strong passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA): Enforce strong password policies and implement MFA to add an extra layer of security during login attempts.
- Antivirus and anti-malware software: Install and maintain up-to-date antivirus and anti-malware software on all devices to detect and prevent malicious software attacks.
- Regular software updates and patching: Regularly update your operating systems, applications, and firmware to address known vulnerabilities and patch security holes.
- Secure Wi-Fi practices: Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks for sensitive transactions and implement strong encryption protocols for your business Wi-Fi.
- Employee cybersecurity awareness training: Educate your employees on cybersecurity best practices, including phishing scams and social engineering tactics.
4. Incident Response Planning
An incident response plan outlines the steps your business will take in the event of a cyberattack. Having a predefined plan ensures a coordinated and efficient response, minimizing damage and downtime.
Remember, building a strong cybersecurity posture is an ongoing process. By following these steps and continuously adapting your strategy, you can significantly enhance your small business’s defenses against cyberattacks.
Additional Considerations for Enhanced Protection

The field of cybersecurity is subject to continuous change, as novel threats and exploitable weaknesses appear frequently. For small businesses, staying informed about these developments is crucial for maintaining a robust defense posture.
Several resources can assist small businesses in staying up-to-date on cybersecurity best practices. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) website offers a wealth of information, including the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, a comprehensive guide for developing effective cybersecurity strategies.
Cyber insurance can be another valuable tool for small businesses. Cyber insurance policies can help mitigate the financial burden associated with cyberattacks, covering costs like data breach notification, legal fees, and credit monitoring. While cyber insurance doesn’t prevent attacks, it can provide a financial safety net in the event of a successful breach.
By staying informed, implementing a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, and considering cyber insurance, small businesses can significantly enhance their digital defenses and foster a more secure environment for themselves and their customers.
Building a Culture of Cybersecurity
While implementing a robust cybersecurity strategy is essential, building a culture of cybersecurity within your small business is equally critical. This proactive approach fosters a shared responsibility for digital security among all employees. Here’s how to cultivate a culture of cybersecurity:
- Regular Cybersecurity Awareness Training: Invest in ongoing cybersecurity awareness training for all employees. Trainings should educate them on the latest cyber threats, phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and best practices for secure online behavior. Regularly updated training fosters a culture of vigilance and preparedness.
- Open Communication Channels: Encourage open communication about cybersecurity concerns. Create a safe space for employees to report suspicious activity or ask questions without fear of reprisal. This fosters trust and empowers them to be active participants in protecting the company’s digital assets.
- Leadership Commitment: Demonstrate strong leadership commitment to cybersecurity. Senior management should actively promote cybersecurity initiatives and highlight their importance to the organization’s success. This sets the tone for the entire company and motivates employees to prioritize cybersecurity measures.
By fostering a culture of cybersecurity, small businesses can significantly enhance their overall security posture. Empowered and informed employees become the first line of defense against cyberattacks, contributing to a more secure and resilient digital environment.
Additional Resources:
- Small Business Administration (SBA): Cybersecurity for Small Businesses (https://www.sba.gov/business-guide/manage-your-business/strengthen-your-cybersecurity)
- The Cybersecurity Framework promulgated by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) (https://www.nist.gov/cyberframework)
How Small Businesses Can Leverage Cybersecurity for Enhanced Protection
Data Privacy Regulations and Your Small Business: What You Need to Know About CCPA/GDPR Compliance.
Remember, cybersecurity is an ongoing process. By continuously adapting your strategy, staying informed about emerging threats, and fostering a culture of security awareness, you can significantly strengthen your small business’s defenses and build lasting resilience against cyberattacks.
Categorized in:
Comments