
The Imperative of Integrated Cloud Security
The exponential growth of cloud computing has fundamentally transformed how businesses operate. Leveraging the scalability and cost-efficiency of cloud platforms, organizations can access powerful computing resources, deploy applications faster, and collaborate seamlessly – all while minimizing upfront infrastructure investments. A report by Gartner predicts that by 2025, over 85% of enterprise workloads will migrate to the cloud. This widespread adoption, however, necessitates a robust cybersecurity posture.
The digital landscape is fraught with evolving cyber threats. In 2023 alone, global cybercrime costs reached an estimated $6 trillion, highlighting the immense financial burden shouldered by businesses. Traditional cybersecurity measures, while crucial, may not be sufficient to safeguard cloud environments that are inherently more dynamic and interconnected.
To effectively navigate this complex landscape, businesses must adopt an integrated approach that merges the strengths of traditional cybersecurity with cloud-specific security solutions. This holistic strategy fosters a layered defense against cyber threats, enhances visibility and control across all environments, and streamlines security management, ultimately leading to a more secure and agile business landscape. For small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), readily available cloud security solutions coupled with a thorough cybersecurity assessment can significantly bolster their defenses without requiring extensive in-house expertise.
The Evolving Threat Landscape: Beyond the Firewall

The contemporary business landscape is besieged by a relentless barrage of cyber threats that constantly evolve in sophistication and scope. Gone are the days of rudimentary malware attacks – today’s cybercriminals employ a diverse arsenal of techniques, meticulously crafting targeted campaigns to exploit vulnerabilities specific to an organization. This necessitates a proactive approach to cybersecurity, moving beyond reactive measures focused on known threats.
The widespread adoption of cloud computing has introduced a new dimension to the threat landscape. Cloud-specific vulnerabilities like data breaches, account hijacking, and insecure APIs present unique challenges. Data breaches, where sensitive information is compromised, can have devastating consequences for an organization’s reputation and financial well-being. Account hijacking, where unauthorized actors gain access to cloud accounts, can be used to deploy malware, steal data, or disrupt operations. Insecure APIs, which act as gateways to cloud applications, can provide a backdoor for unauthorized access if not properly secured.
Traditional security measures, while still crucial, may be insufficient to combat these evolving threats. Firewalls, for instance, are adept at blocking basic malware but may struggle to detect more sophisticated attacks. Similarly, legacy antivirus software might not be equipped to identify and neutralize zero-day exploits – vulnerabilities unknown to security vendors. This highlights the need for a comprehensive security strategy that integrates traditional approaches with cloud-specific security solutions.
The gravity of the cyber threat is underscored by the staggering financial burden it places on businesses. According to a report by the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), global cybercrime costs reached an estimated $6 trillion in 2023. This alarming statistic underscores the critical need for businesses, particularly small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), to conduct regular security gap analyses and explore cybersecurity services to bolster their defenses. By proactively identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, organizations can significantly reduce their cyber risk exposure.
Traditional Cybersecurity Approaches

Traditional cybersecurity approaches form the bedrock of a robust security posture, laying the groundwork for effective cloud security integration. These time-tested methods provide essential layers of defense against a range of cyber threats.
- Firewalls: Functioning as digital gatekeepers, firewalls monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic, filtering out malicious activity based on predefined rules. While firewalls excel at blocking basic threats, they may struggle to identify more nuanced attacks.
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): These systems continuously monitor network activity for suspicious behavior, triggering alerts or automatically blocking potentially harmful attempts to access a system. However, IDS/IPS systems can generate a significant number of false positives, requiring ongoing analysis and configuration.
- Anti-virus and Anti-malware software: These programs scan devices and networks for malicious software, quarantining or removing threats upon detection. While effective against known malware strains, they may not be able to identify novel or zero-day threats.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): ACLs dictate which users or systems have access to specific resources, establishing permission boundaries within a network. ACLs offer granular control, but managing them can become complex as an organization grows.
- Data encryption: This process scrambles data using a cryptographic key, rendering it unreadable to unauthorized parties. Data encryption safeguards sensitive information at rest (stored on a device) and in transit (being transmitted over a network). Nevertheless, the efficacy of encryption depends on the implementation of strong key management practices.
- Security awareness training for employees: Educating employees about cyber threats and best practices is crucial. Regular training can equip employees to identify phishing attempts, avoid suspicious links, and report security incidents promptly. However, the effectiveness of training programs hinges on ongoing reinforcement and tailored content.
These traditional methods, while not without limitations, provide a strong foundation for cloud security. By understanding and implementing these core cybersecurity principles, organizations establish a baseline level of protection that can be further enhanced with cloud-specific security solutions. A security gap analysis, a systematic review of an organization’s security posture, can be a valuable tool for identifying areas where traditional methods can be strengthened or supplemented with cloud-based solutions. For small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), readily available security assessment services can provide valuable insights to optimize their cybersecurity posture for the cloud era.
Cloud Security Solutions: Safeguarding the Digital Vault

Cloud providers offer a robust arsenal of security solutions specifically designed to fortify cloud environments. These solutions work in harmony with traditional methods to create a comprehensive security posture. Here’s a closer look at some key cloud security solutions:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM serves as the digital gatekeeper for cloud resources, meticulously controlling access privileges. It enables organizations to define who can access specific resources, what actions they can perform, and under what circumstances. This granular control over access minimizes the risk of unauthorized activity and data breaches.
- Data Encryption at Rest and In Transit: Cloud providers offer robust data encryption solutions that scramble data both while it resides in cloud storage (at rest) and while it’s being transmitted (in transit). This encryption ensures that even if unauthorized actors gain access to data, they’ll be unable to decipher it without the decryption key.
- Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPPPs): These comprehensive platforms offer a multi-layered defense against threats targeting cloud workloads. CWPPPs typically include features like vulnerability scanning, intrusion detection, and workload isolation to safeguard cloud-based applications and virtual machines.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) for Cloud Logs: SIEM solutions act as the central nervous system for security operations, collecting and analyzing security logs generated across various cloud resources. By correlating these logs in real-time, SIEM can identify suspicious activity and potential security incidents, enabling a rapid response.
- Vulnerability Scanning and Patching for Cloud Resources: Cloud providers offer automated vulnerability scanning tools that identify weaknesses in cloud environments. These tools work in conjunction with patch management solutions to automatically deploy security patches, proactively addressing vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
| Cloud Security Solution | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Identity and Access Management (IAM) | Granular control of access privileges to cloud resources |
| Data Encryption (at rest & in transit) | Protects data confidentiality by rendering it unreadable without a decryption key |
| Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPPPs) | Multi-layered defense against threats targeting cloud workloads |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) for Cloud Logs | Real-time analysis of security logs to identify suspicious activity |
| Vulnerability Scanning and Patching | Proactive identification and remediation of vulnerabilities in cloud resources |
By implementing these cloud security solutions alongside traditional methods, businesses can significantly enhance their overall security posture. Regular security gap assessments can help identify potential weaknesses and ensure that these solutions are effectively deployed. This comprehensive approach empowers businesses to confidently leverage the power and scalability of the cloud while mitigating associated security risks.
Empowering Small Businesses with Cloud Security
Cloud security solutions offer a multitude of advantages, but for small businesses, these benefits can be particularly impactful. To delve deeper into how cloud security can optimize operational efficiency and empower small businesses to navigate the digital landscape with confidence, explore our companion article: [Optimizing Small Business Operations with Cloud Security Solutions]. This comprehensive guide explores the unique challenges faced by small businesses and offers practical guidance on leveraging cloud security solutions to achieve their growth objectives.
Integrating Cloud Security with Traditional Approache

Optimizing security in today’s hybrid IT landscape hinges on effectively integrating cloud security solutions with traditional cybersecurity practices. This holistic approach fosters a layered defense, providing comprehensive protection against evolving cyber threats. Let’s delve into key strategies for successful integration:
- Unified Security Policy: Develop a comprehensive security policy that encompasses both on-premises and cloud environments. This policy should clearly define acceptable use practices, access control protocols, data security measures, and incident response procedures. A unified policy ensures consistency and reduces the risk of security gaps arising from disparate approaches.
- Centralized Management: Embrace cloud security tools that integrate seamlessly with existing security management platforms (SMPs). This centralized management approach streamlines security operations, offering a unified view of security posture across all environments. By leveraging a single pane of glass, security teams can efficiently monitor activity, identify threats, and orchestrate incident response efforts.
- Threat Intelligence Sharing: Foster a continuous exchange of threat intelligence between traditional and cloud security systems. Security information and event management (SIEM) solutions can play a pivotal role in this process, correlating data from diverse sources to identify emerging threats and potential vulnerabilities. Sharing threat intelligence empowers both systems to adapt and proactively defend against the latest cyberattacks.
- Continuous Monitoring and Logging: Implement continuous monitoring of both cloud and on-premises systems for suspicious activity. Security teams should leverage log management tools to collect, analyze, and correlate log data from various sources. This comprehensive approach enables them to detect anomalies, investigate potential security incidents, and identify potential attack vectors before they can be exploited.
- Regular Security Assessments and Testing: Schedule regular penetration testing and vulnerability assessments for both traditional and cloud infrastructure. These proactive measures help identify weaknesses in security posture and ensure that deployed security solutions are functioning effectively. By simulating real-world attacks, penetration testing can expose potential security gaps that might otherwise remain undetected.
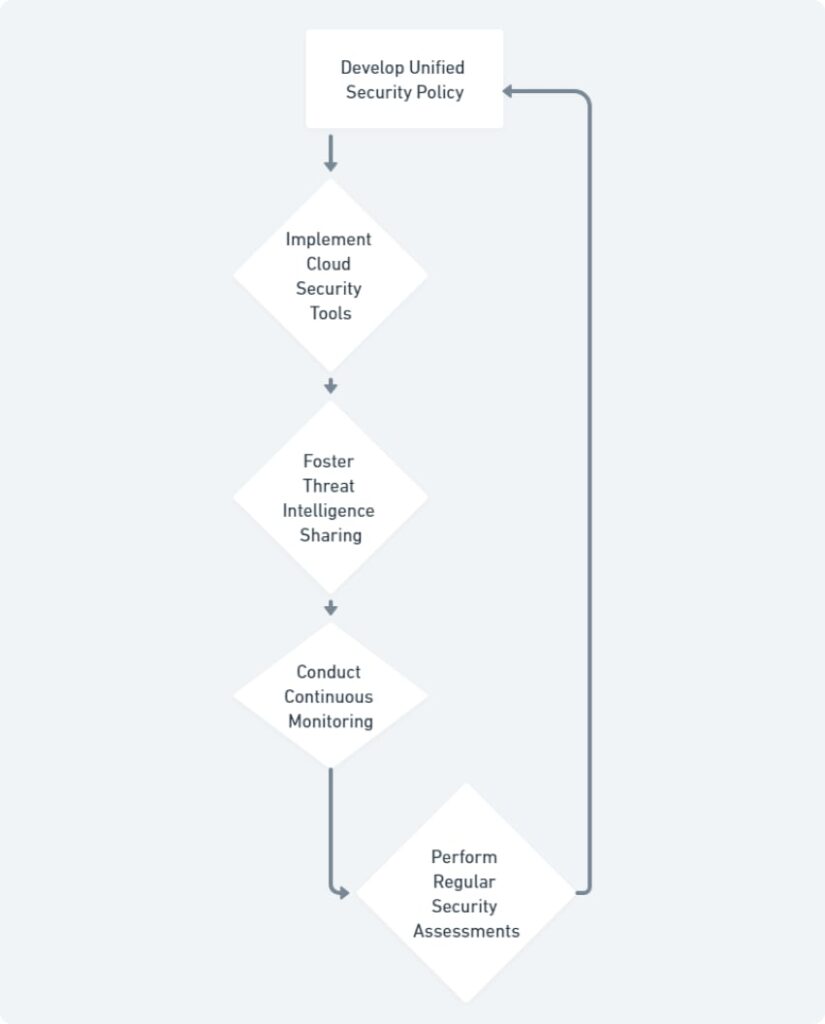
By following these integration strategies and leveraging the visual representation provided by the flowchart, businesses can establish a robust and well-coordinated security posture. This empowers them to not only prevent data breaches but also navigate the ever-changing threat landscape with greater confidence. For small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), consulting with cybersecurity professionals can be invaluable in choosing the best cybersecurity solution tailored to their specific needs and effectively integrating it with existing security measures.
Benefits of an Integrated Approach

Integrating cloud security with traditional approaches unlocks a multitude of advantages, empowering businesses to navigate the complex threat landscape with greater confidence. Here’s a closer look at some key benefits:
- Enhanced Security Posture: By combining the strengths of traditional security methods with advanced cloud security solutions, organizations establish a robust, layered defense. This comprehensive approach mitigates the risk of cyberattacks by addressing vulnerabilities across all environments.
- Improved Visibility and Control: Integrated security offers a centralized view of security posture across both cloud and on-premises infrastructure. This enhanced visibility empowers security teams to identify and address threats more effectively, streamlining incident response and improving overall control.
- Streamlined Security Management: Leveraging cloud security tools that integrate with existing security management platforms fosters a more efficient approach to security operations. This reduces administrative overhead and simplifies security management, allowing IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Increased Agility and Scalability: An integrated approach empowers businesses to embrace new cloud technologies with greater confidence, knowing that their security posture remains robust. This agility and scalability are crucial for businesses operating in today’s dynamic and ever-evolving digital landscape.
For small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), this integrated approach can be particularly advantageous. Many cloud providers offer free cybersecurity resources and tools to help them get started. Additionally, consulting with cybersecurity professionals can guide them in choosing the best cybersecurity solution tailored to their specific needs and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
A Unified Defense in the Digital Age
The ever-expanding digital landscape necessitates a robust and adaptable security posture. Integrating cloud security with traditional approaches fosters a comprehensive defense, empowering businesses to navigate the evolving threat landscape with greater confidence. By establishing a unified security policy, implementing best-in-breed security solutions, and fostering continuous monitoring and assessment, businesses can significantly reduce their security risks. We encourage organizations to proactively evaluate their current security posture and leverage the numerous benefits offered by an integrated approach. Numerous resources, including free cybersecurity tools and professional consultations, are available to assist businesses in securing their digital assets. Taking these steps demonstrates a proactive commitment to cybersecurity, safeguarding valuable data and fostering a secure environment for continued growth and success.
Categorized in:
Comments