
The deep web and dark web are often misunderstood terms, yet differentiating between them is essential, particularly for businesses in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) seeking to strengthen their cybersecurity posture. The deep web refers to a vast portion of the internet that contains legitimate, non-indexed content, such as medical records, financial statements, and internal business databases. This information is accessible through private logins or secured networks but is not available to the general public via search engines.
In contrast, the dark web is a smaller, hidden subset of the internet that is often associated with illegal activities. Accessible only through specialized browsers like Tor, the dark web is notorious for the sale of stolen data, ransomware services, and other cybercrime activities. Understanding the nature of these two entities is crucial for UAE businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), because threats from the dark web can significantly compromise a company’s operations and reputation.
As cybercrime continues to grow, cybersecurity for businesses—especially small businesses—must evolve to address the risks posed by data breaches, ransomware, and credential theft often facilitated through the dark web. Conducting regular cybersecurity assessments and leveraging dark web intelligence services can help identify potential vulnerabilities and prevent attacks before they happen. This knowledge is vital to safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining compliance with cybersecurity regulations in the UAE.
By understanding the differences between the deep web and dark web, UAE businesses can better anticipate and mitigate the top cybersecurity threats they face, protecting their operations and customer data from illicit activities.
Understanding the Deep Web
The deep web consists of non-public databases, private information behind login forms, and subscription-based content that is not indexed by search engines like Google or Bing. This part of the internet contains sensitive but legitimate content, such as internal business records, academic databases, and personal financial information. Unlike the surface web, which is publicly accessible and easily searchable, the deep web requires specific credentials or subscriptions to gain access.
While the deep web is not inherently harmful, it hosts vast amounts of sensitive data, making it a potential target for cybercriminals. For example, confidential business documents, employee records, or customer information stored on internal systems are part of the deep web. Therefore, cybersecurity for businesses must focus on securing these access points to ensure unauthorized users cannot infiltrate these areas. A strong cybersecurity assessment should identify and fortify any vulnerabilities that may expose a business’s deep web content to external threats.
A key concept to understand is that the deep web itself is a secure part of the internet; however, inadequate protection, such as weak authentication systems or poorly encrypted databases, can lead to data breaches. Businesses need to perform regular security gap assessments to identify areas where their data could be at risk and implement necessary measures, such as multi-factor authentication and data encryption. Securing these access points will significantly reduce exposure to threats that could lead to a data breach, even from a non-public part of the internet.

By ensuring that sensitive data within the deep web is well-protected, businesses can safeguard their operations and comply with cybersecurity regulations, thus reducing the risk of potential threats.
What is the Dark Web?
The dark web is a hidden layer of the internet that is inaccessible through standard search engines or browsers. Unlike the deep web, which contains legitimate, non-indexed content such as private databases and internal business records, the dark web is often associated with illicit activities. Users access the dark web through specialized browsers like Tor, which anonymize their presence and make it difficult to trace activities or users. This anonymity has made the dark web a haven for cybercriminals who use it to sell stolen data, distribute ransomware kits, and trade in illegal goods such as drugs and weapons.
One of the most significant risks posed by the dark web is the sale of compromised business data. Hackers frequently post stolen credentials, credit card information, and intellectual property on dark web forums, making it easy for malicious actors to exploit small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). For UAE businesses, understanding the dark web’s role in facilitating cybercrime is essential. Hackers often target smaller businesses due to their weaker security infrastructures, making cybersecurity for small businesses a critical concern.
Ransomware attacks are another threat originating from the dark web. Hackers often sell ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) kits, allowing even non-technical criminals to launch devastating attacks on businesses. These attacks typically encrypt a company’s critical data, demanding a ransom for its release. This is one of the top cybersecurity threats small businesses face today, and without adequate security measures, recovering from such an attack can be both costly and damaging to a company’s reputation.
Given the growing number of threats emerging from the dark web, UAE businesses must invest in cybersecurity services for small businesses. Regular cybersecurity assessments and ongoing monitoring of dark web activity can help detect compromised credentials or vulnerabilities early, enabling companies to take preventive action before a full-scale attack occurs.

By staying informed and actively monitoring dark web activities, businesses can better protect themselves from evolving cyber threats, safeguarding their operations and data.
The Rising Threat of Cybercrime from the Dark Web
UAE businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), face increasing cyber threats originating from the dark web. Cybercriminals use the dark web to trade stolen credentials, deploy phishing schemes, and sell ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) platforms, making it easier for attackers to target businesses of all sizes. These tools, once limited to sophisticated hackers, are now widely accessible to a broader audience of criminals.
Ransomware, for instance, is one of the most devastating dark web-facilitated threats. Attackers use RaaS platforms to encrypt critical business data, demanding payment for decryption. SMEs often lack the resources and cybersecurity defenses to recover quickly from such attacks, resulting in significant financial losses and potential reputational damage. Phishing schemes, another prevalent threat, can steal sensitive business information, including login credentials, financial details, and customer data, often found for sale on dark web marketplaces.
In the UAE, SMEs are particularly vulnerable due to limited cybersecurity infrastructures compared to larger enterprises. Without a strong cybersecurity framework in place, businesses risk falling victim to these attacks, leading to severe operational disruptions. To mitigate these threats, companies must prioritize the best cybersecurity for small business, including regular cybersecurity assessments and adopting comprehensive solutions to prevent data breaches.
The table below outlines common dark web threats and their impact on UAE businesses:
| Threat Type | Description | Impact on UAE Businesses |
|---|---|---|
| Ransomware | Malicious software that encrypts data for ransom | Data loss, financial loss, and reputational damage |
| Phishing | Fraudulent attempts to steal sensitive information | Compromised credentials, financial fraud |
| Stolen Credentials | Sale of business login and access credentials | Unauthorized access, potential data breaches |
| Data Breaches | Exposure of sensitive business or customer data | Legal penalties, reputational damage |
To avoid these risks, businesses must choose the best cybersecurity solutions for small businesses, combining prevention, monitoring, and quick-response capabilities to protect their operations.
How Dark Web Intelligence Protects Businesses

Dark web intelligence has become an invaluable tool for UAE businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), in mitigating emerging cyber threats. Cybercriminals use the dark web to trade stolen data, plan ransomware attacks, and sell malicious tools, often targeting businesses with weak cybersecurity defenses. By leveraging cybersecurity services for small businesses that include dark web intelligence, organizations can stay one step ahead of potential threats.
One of the most effective steps a company can take is conducting a comprehensive cybersecurity assessment. This assessment helps identify existing vulnerabilities, such as exposed login credentials, weak password policies, or outdated software, that could be exploited by dark web actors. Once risks are uncovered, businesses can address these weaknesses proactively to reduce their exposure to attacks.
Several cybersecurity firms offer specialized dark web intelligence services tailored to the needs of small businesses. Companies like Recorded Future and Group-IB provide threat intelligence feeds that monitor the dark web for mentions of company domains, employee credentials, or sensitive information. This continuous monitoring allows businesses to act swiftly to neutralize threats. Coupling this with a security gap analysis ensures that the organization’s overall cybersecurity posture is aligned with best practices, offering a robust defense.
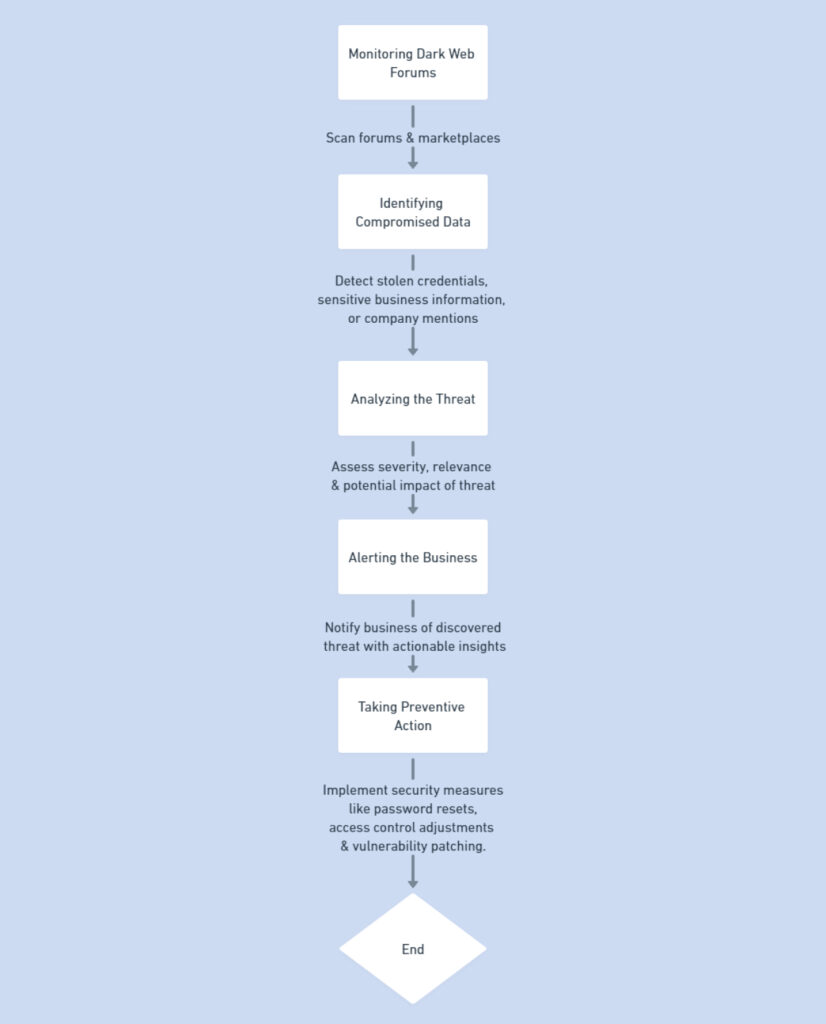
By integrating dark web intelligence into their cybersecurity strategy, businesses can not only detect risks early but also respond effectively, thereby preventing data breaches, ransomware attacks, and other costly cyber threats.
Cybersecurity Best Practices for UAE Businesses
To safeguard against rising cyber threats originating from the dark web, UAE businesses must implement a range of essential cybersecurity best practices. These measures are particularly critical for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which often lack the extensive security infrastructure of larger corporations. By adopting a proactive approach, businesses can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to cyberattacks.
A key starting point is conducting regular cybersecurity risk assessments. These evaluations help identify potential vulnerabilities in the system, allowing businesses to address weaknesses before they can be exploited. Complementary to this, a security gap analysis provides an in-depth review of an organization’s security measures versus best practices, highlighting areas that need improvement.
Implementing strong password policies is another vital practice. Employees should be required to use complex, unique passwords, regularly updated to reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) further strengthens security by requiring an additional layer of verification, ensuring that even if a password is compromised, access is still restricted.
Businesses should also regularly back up critical data to prevent loss in the event of a ransomware attack. Storing these backups in secure, isolated environments ensures data can be recovered without paying a ransom. Utilizing tools like encryption and firewalls helps protect sensitive information and keep cybercriminals out of the system.
UAE companies must also focus on compliance with local cybersecurity regulations, such as those mandated by the Telecommunications and Digital Government Regulatory Authority (TDRA). Compliance not only helps avoid legal penalties but also ensures that businesses meet stringent security standards.
| Cybersecurity Best Practice | Recommended Tools |
|---|---|
| Cybersecurity Risk Assessment | Vulnerability scanners, threat intelligence tools |
| Security Gap Analysis | Gap analysis software, compliance checklists |
| Strong Password Policies | Password managers (e.g., LastPass, 1Password) |
| Multi-Factor Authentication | MFA solutions (e.g., Google Authenticator, Duo) |
| Regular Data Backups | Backup solutions (e.g., Veeam, Acronis) |
| Encryption & Firewalls | Encryption tools (e.g., BitLocker), firewalls (e.g., Fortinet) |
| Compliance with UAE Cybersecurity Regulations | TDRA guidelines, legal compliance audits |
By implementing these best practices, UAE businesses can effectively comply with cybersecurity regulations, mitigate risks, and prevent data breaches that could lead to severe financial and reputational damage.
Choosing the Right Cybersecurity Solutions for Your Business

Selecting the best cybersecurity solutions for your business in the UAE requires a thoughtful approach based on your organization’s specific needs. Factors such as budget, the size of operations, and industry-specific regulations must be carefully considered. For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), the focus should be on scalability—solutions that can grow with the business as cybersecurity needs evolve.
Budget plays a key role in the decision-making process, but cutting costs by opting for minimal protection can leave businesses vulnerable to attacks. Instead, businesses should seek cybersecurity services for small businesses that offer customizable packages, ensuring cost-effective yet comprehensive protection.
The scale of operations should guide the selection of services that provide adequate coverage, from basic firewall protection and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to advanced threat monitoring. For SMEs, scalability is crucial—solutions should adapt as the business grows without causing significant financial strain.
It’s also essential to comply with cybersecurity regulations set forth by UAE authorities, such as the Telecommunications and Digital Government Regulatory Authority (TDRA). Companies should ensure that the cybersecurity solution aligns with these regulatory requirements and performs regular cybersecurity assessments to remain compliant.
By choosing a solution that integrates security gap analysis, threat intelligence, and compliance, businesses can effectively mitigate risks. Ultimately, the best cybersecurity solutions for small businesses are those that balance cost-efficiency, scalability, and robust protection.
In conclusion, UAE businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), face increasing cyber threats from the dark web. By understanding the risks associated with stolen data, ransomware attacks, and other dark web activities, companies can better protect themselves. Implementing regular cybersecurity risk assessments is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities and preventing data breaches.
Dark web monitoring is an equally important measure that allows businesses to detect potential threats early, reducing the risk of damage from cyberattacks. Services like threat intelligence and security gap analysis offer valuable insights that can help organizations proactively improve their cybersecurity infrastructure.
All businesses, regardless of size, must adopt a proactive and strategic approach to cybersecurity for businesses to stay protected. Regular cybersecurity assessments, strong data protection policies, and compliance with UAE’s cybersecurity regulations, such as those outlined by the Telecommunications and Digital Government Regulatory Authority (TDRA), are essential steps in this process. By choosing the best cybersecurity solutions for small businesses, companies can mitigate risks and ensure their long-term resilience in the face of evolving cyber threats.
By understanding the differences between the deep web and dark web, UAE businesses can better anticipate and mitigate the top cybersecurity threats they face, protecting their operations and customer data from illicit activities. However, the fight against cybercrime is constantly evolving. To learn more about how artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are revolutionizing cybersecurity processes, empowering businesses to streamline defenses and strengthen threat detection, visit our follow-up article: [Exploring the Role of AI and Automation in Streamlining Cybersecurity Processes].
Categorized in:
Comments