
Cybersecurity Imperative in the Digital Age
The contemporary business landscape is demonstrably shaped by the ever expanding digital domain. As more critical operations and sensitive data migrate online, cybersecurity has become an imperative, not merely an optional safeguard. The interconnected nature of the digital world fosters an environment rife with cyber threats, constantly evolving in sophistication and posing a significant financial and reputational risk to organizations.
A report by Cybersecurity Ventures predicts global cybercrime costs to reach a staggering $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, highlighting the magnitude of the financial burden. Furthermore, recent data breaches affecting major corporations underscore the potential for reputational damage and loss of consumer trust in the wake of a cyberattack.
Recognizing this evolving threat landscape, regulatory bodies across various industries have implemented stricter legal frameworks. These regulations mandate specific cybersecurity protocols to ensure the protection of sensitive data and critical infrastructure. For instance, the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) safeguards financial information within the US financial sector, while the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) governs the security of medical data in the healthcare industry.
Navigating this complex web of regulations necessitates a nuanced approach. Businesses must tailor their cybersecurity strategies to effectively address the unique compliance requirements dictated by their industry. By adhering to industry-specific regulations and implementing robust cybersecurity measures, organizations can bolster their defenses against cyberattacks, mitigate financial losses, and safeguard their reputation in the digital age.
Understanding Industry-Specific Regulations

The Regulatory Landscape and Data Security
The burgeoning digital age necessitates a robust legal framework to safeguard sensitive information entrusted to organizations across various industries. Industry-specific regulations serve as the cornerstone of data protection and security, outlining mandatory protocols for handling confidential information and safeguarding critical infrastructure. These regulations function as a standardized approach, ensuring a baseline level of cybersecurity measures across different sectors.
Examples of Key Regulations
The following table illustrates prominent regulations within specific industries:
| Industry | Regulation | Description | Relevant Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Services | Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) | Protects the privacy of financial information for consumers. | Link |
| Financial Services | Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) | Outlines security requirements for organizations that handle cardholder data. | Link |
| Healthcare | Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) | Safeguards the privacy and security of protected health information (PHI). | Link |
| Energy and Utilities | North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) Standards | Enforce security measures to protect the bulk power system. | Link |
Consequences of Non-Compliance

Failure to adhere to industry-specific regulations can incur significant repercussions for organizations. These consequences encompass:
- Financial Penalties: Regulatory bodies may impose hefty fines on non-compliant entities.
- Reputational Damage: Data breaches and security incidents stemming from non-compliance can severely tarnish an organization’s reputation, potentially leading to loss of customer trust and market share.
- Legal Repercussions: In egregious cases, non-compliance can lead to legal action, including lawsuits and criminal charges.
The Interplay Between Regulations and Cybersecurity Assessments
Understanding industry-specific regulations is crucial for conducting thorough cybersecurity assessments. By aligning their risk assessments with the mandated security protocols outlined in the relevant regulations, businesses can effectively identify vulnerabilities and prioritize mitigation strategies.
Addressing the Needs of Small Businesses
Numerous free cybersecurity resources are available for small businesses, including those offered by government agencies and industry associations. These resources can provide valuable guidance on understanding industry regulations, conducting security assessments, and implementing essential cybersecurity measures.
Conducting a Cybersecurity Risk Assessment

A cybersecurity risk assessment serves as a systematic method for proactively identifying vulnerabilities within an organization’s IT infrastructure and data security posture. This comprehensive evaluation plays a critical role in safeguarding sensitive information and mitigating the potential consequences of cyberattacks.
Key Steps in a Risk Assessment
- Identifying Assets: The initial step involves meticulously cataloging all critical assets, encompassing data (customer information, financial records), systems (servers, databases), and infrastructure (network devices, workstations). Understanding the value and sensitivity of these assets forms the foundation for prioritizing risk mitigation efforts.
- Threat Identification: A thorough analysis of potential threats and attack vectors specific to the industry is crucial. This involves considering common cyber threats like malware, phishing attacks, and unauthorized access attempts, while also acknowledging industry-specific vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Following the identification of threats, a systematic evaluation of weaknesses within systems and processes must be conducted. This assessment may involve penetration testing to simulate cyberattacks and identify exploitable security gaps.
- Risk Prioritization: Having identified potential threats and vulnerabilities, the likelihood and potential impact of a security breach for each asset must be meticulously evaluated. This prioritization enables businesses to allocate resources effectively towards addressing the most critical risks.
Accessibility of Cybersecurity Resources
Recognizing the challenges faced by small businesses, numerous government agencies and industry associations offer free cybersecurity resources. These resources provide valuable guidance on conducting security gap assessments, understanding industry-specific regulations, and implementing essential cybersecurity measures.
Addressing the Challenges of Small Businesses

While larger organizations may have dedicated cybersecurity teams, small businesses often face resource constraints. Fortunately, numerous freely available resources exist to assist them.
- Government agencies and industry associations offer various materials, including:
- Online guides explaining industry-specific regulations and best practices.
- Webinars and workshops provide practical guidance on conducting security assessments.
- Templates and checklists to streamline the implementation of essential cybersecurity measures.
These resources empower small businesses to gain a foundational understanding of cybersecurity threats, navigate regulatory requirements, and implement basic security controls to protect their data and infrastructure.
Additional Support
For situations requiring a more comprehensive approach, several managed security service providers (MSSPs) cater specifically to the needs of small businesses. These providers offer a range of services, including:
- Vulnerability assessments to identify and prioritize security weaknesses.
- Ongoing monitoring and threat detection to proactively address potential cyberattacks.
- Incident response assistance to guide businesses through security breaches and minimize damage.
By leveraging a combination of free resources and professional support when needed, small businesses can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture and operate with greater confidence in the digital landscape.
Building a Tailored Cybersecurity Strategy

In the dynamic landscape of cybersecurity threats, a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy tailored to address industry-specific regulations forms the cornerstone of an organization’s defense. Regulatory compliance mandates specific security protocols, and aligning the cybersecurity strategy with these requirements ensures adherence to legal frameworks and minimizes the risk of hefty fines and reputational damage.
Elements of a Tailored Strategy
- Access Controls: Implementing robust authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), and enforcing authorization protocols that restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles, significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Data Security: Encrypting data at rest and in transit safeguards sensitive information even in the event of a security breach. Encryption renders the data unreadable without the appropriate decryption key, significantly hindering unauthorized access and mitigating the potential consequences of a cyberattack.
- Network Security: Firewalls act as the first line of defense, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic to block malicious activity. Additionally, Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) continuously monitor network activity for suspicious behavior and can automatically take corrective actions to prevent cyberattacks.
- Employee Training: Regular awareness programs equip employees with the knowledge and skills to identify and respond to potential cyber threats. Educating employees on phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and secure password practices is crucial in mitigating the risk of human error.
- Incident Response Plan: A pre-defined incident response plan establishes a structured approach for effectively handling security breaches. This plan should outline clear roles and responsibilities for personnel involved, communication protocols for notifying stakeholders, and procedures for containment, eradication, and recovery efforts.
Visualizing the Incident Response Process
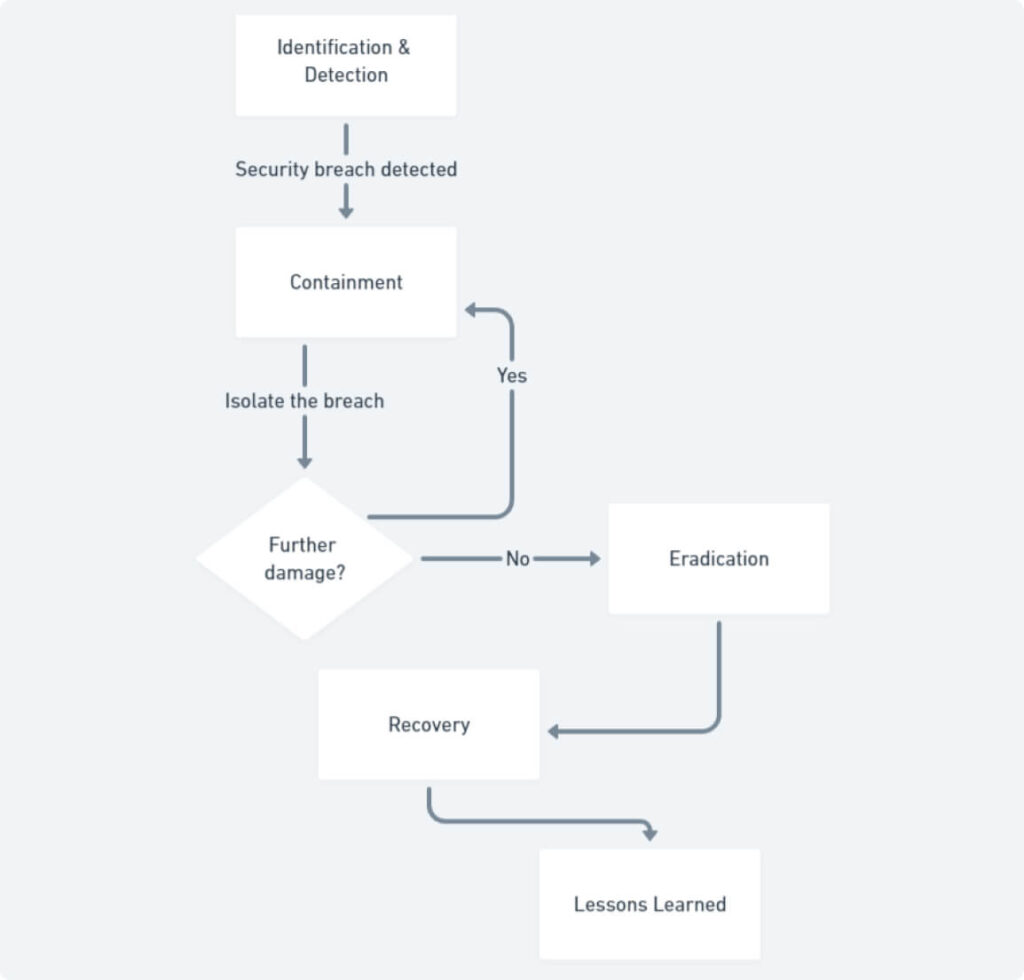
- Identification & Detection: Identifying a potential security breach through internal monitoring, security alerts, or external reports.
- Containment: Taking immediate action to isolate the breach and prevent further damage, such as shutting down affected systems.
- Eradication: Removing the source of the threat, such as malicious software or unauthorized access.
- Recovery: Restoring affected systems and data to a functional state.
- Lessons Learned: Analyzing the incident to identify vulnerabilities and improve future response strategies.
For small businesses, navigating the intricacies of cybersecurity regulations can be a daunting task. To simplify this process, we recommend a helpful resource titled Complying with Cybersecurity Regulations: A Simplified Guide for Small Businesses. This comprehensive guide offers a step-by-step approach to achieving compliance and outlines essential security measures to safeguard your critical data.
In conclusion, navigating the intricate landscape of cybersecurity regulations necessitates a multifaceted approach. Tailoring a cybersecurity strategy that adheres to industry-specific regulations and incorporates robust security measures is fundamental for safeguarding sensitive information and mitigating cyber risks.
This strategy should encompass elements like access controls, data encryption, network security, and employee training. Regular security testing, including penetration testing which simulates real-world attacks, is crucial for proactively identifying vulnerabilities.
For organizations lacking internal expertise, collaborating with Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) can provide comprehensive support and ongoing threat management. By continuous monitoring, improving, and adapting their cybersecurity posture, businesses can foster a secure digital environment and operate with greater confidence in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Categorized in:
Comments