
Securing SMBs in the Digital Age Without Sacrificing User Experience
The ever-expanding digital landscape presents a double edged sword for businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMBs). While it unlocks a world of opportunity for growth and innovation, it also exposes them to a heightened risk of cyberattacks. A 2023 study by Verizon found that 43% of all cyberattacks target small businesses, often due to the perception of weaker defenses.
The consequences of a successful cyberattack can be devastating. Data breaches can expose sensitive customer information, intellectual property and financial records, leading to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and even legal repercussions for non-compliance with data privacy regulations.
However, fortifying cybersecurity measures doesn’t have to come at the cost of user experience (UX). Imagine a customer attempting to access their account on your platform, only to be met with a labyrinth of complex login steps. This frustration can lead to cart abandonment or account creation dropout, ultimately hindering business growth.
This article aims to bridge this gap. We’ll delve into the strategies for implementing secure login processes that prioritize both robust security and a seamless user experience. By adopting a multi-layered approach and leveraging user-centric design principles, businesses can ensure their login systems remain a strong first line of defense without compromising customer satisfaction.
The Importance of Secure Login Processes

Login processes act as the frontline defense against unauthorized access to a business’s digital assets. A thorough security gap analysis can reveal weaknesses in login protocols, highlighting the importance of robust authentication measures. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) emphasizes the critical role of authentication in their Cybersecurity Framework, stating that “effective identity management and access control are the foundation for protecting information assets.” (https://www.nist.gov/cyberframework)
The threat landscape is constantly evolving, with cybercriminals employing increasingly sophisticated tactics to gain unauthorized access. A 2023 report by the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) (https://www.enisa.europa.eu/publications) found a significant rise in phishing attacks, where attackers attempt to trick users into revealing login credentials by mimicking legitimate websites or emails. Furthermore, weak passwords remain a major vulnerability. According to a 2022 study by Verizon, 80% of data breaches involved compromised passwords, highlighting the urgent need for stricter password policies and user education on password hygiene.
A successful breach of login credentials can have disastrous consequences. Hackers can gain access to sensitive customer data, intellectual property, and financial records. This can lead to a domino effect of financial losses, reputational damage and even legal repercussions for non-compliance with data privacy regulations For businesses of all sizes, but particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMBs) with potentially less robust security infrastructure, securing login processes is paramount in safeguarding their digital assets and fostering trust with their customers.
Balancing Security and User Experience

Crafting a secure login process that prioritizes user experience (UX) can feel like navigating a tightrope. Overly complex logins laden with multi-step verifications and cryptic password requirements can leave users frustrated and abandoning attempts altogether. This frustration can even lead to risky workarounds, such as password sharing or writing credentials down, ultimately undermining the very security the process aims to achieve.
A security gap analysis can unveil areas where complexity hinders user experience. Businesses can then implement a more nuanced approach known as risk-based authentication. Here, security measures adapt to the perceived risk associated with a login attempt. For example, a login attempt from a recognized device and usual location might require only a password, while an attempt from an unfamiliar IP address might trigger additional verification steps like multi-factor authentication (MFA). This strategy maintains a harmonious equilibrium between security measures and user convenience.
UX design principles play a crucial role in optimizing login flows without compromising effectiveness. Clear and concise instructions guide users through the process, while intuitive interfaces minimize the potential for errors. Progress bars or visual cues can alleviate frustration during multi-factor authentication, and offering alternative login methods like social logins (with user consent and proper security protocols) can further streamline the experience for familiar users.
Remember, security shouldn’t feel like an obstacle course for legitimate users. By incorporating user-centric design principles and leveraging risk-based authentication, businesses can create a login experience that fosters trust and facilitates secure access. This not only protects valuable data but also enhances user satisfaction, contributing to a positive brand image.
Secure Login Practices - A Multi-Layered Approach
Building a robust login system requires a multi-layered approach, utilizing a combination of methods to create a strong defense against unauthorized access. Here’s a breakdown of some key practices:

1. Strong Password Policies and User Education
- Enforce complex password requirements, mandating a minimum length, character variety (uppercase, lowercase, numbers, symbols), and regular password updates.
- Educate users on password hygiene practices, emphasizing the importance of avoiding easily guessable information and using unique passwords for each account. Password management tools can further strengthen password security by generating and storing complex passwords.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA enhances security by necessitating an additional verification factor alongside the password. Here’s a breakdown of common MFA methods:
- SMS Verification: A one-time code sent via text message to a registered phone number. (Pros: Widely accessible, easy to set up. Cons: Vulnerable to SIM swapping attacks)
- Authenticator Apps: These generate time-based one-time codes on a user’s smartphone. (Pros: More secure than SMS, readily available. Cons: Requires users to have a smartphone)
- Security Keys: Physical tokens that connect to a device’s USB port or use Bluetooth to verify login attempts. (Pros: Most secure MFA method. Cons: Requires additional hardware, may not be compatible with all devices)
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| SMS Verification | Widely accessible, easy to set up | Vulnerable to SIM swapping attacks |
| Authenticator Apps | More secure than SMS, readily available | Requires users to have a smartphone |
| Security Keys | Most secure MFA method | Requires additional hardware, may not be compatible with all devices |
3. Biometric Authentication
Fingerprint and facial recognition are emerging as potential login methods, offering a convenient user experience. However, these technologies are not foolproof and can be susceptible to spoofing attempts.
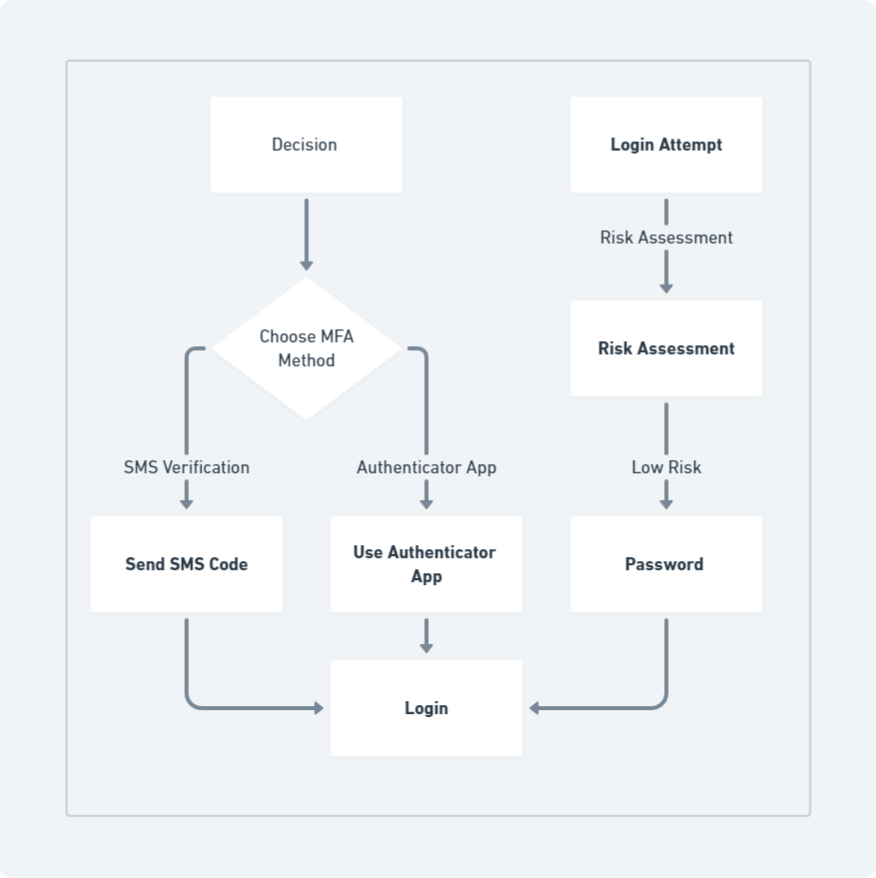
By implementing a combination of these practices and tailoring security measures based on perceived risk, businesses can create a secure login process that doesn’t compromise user experience. Remember, ongoing user education on cybersecurity best practices remains crucial in maintaining a strong defense against cyberattacks.
Even with robust login security measures in place, businesses must remain vigilant against social engineering tactics like phishing attacks. Phishing emails can trick users into revealing their login credentials, bypassing security protocols. To learn more about phishing attacks and how to defend against them, see our article on Phishing Attacks: The Biggest Threat to Small Businesses and How to Stop Them.
Optimizing the Login Experience

The key to a successful login experience lies in striking a balance between security and user-friendliness. Here are some actionable tips:
- Clarity is King: Provide clear and concise instructions throughout the login process. Error messages should be informative, guiding users towards a solution rather than simply stating there’s a problem.
- Less is More: Streamline the login interface by minimizing unnecessary fields or steps. Users shouldn’t feel overwhelmed by a complex layout.
- Recovery with Security: Offer a user-friendly password recovery process, but prioritize security best practices. Multi-factor authentication can be implemented during password resets for an extra layer of protection.
For trusted users who frequently access multiple applications within your ecosystem, consider implementing Single Sign-On (SSO). SSO allows users to log in once and seamlessly access various platforms without repeatedly entering credentials, enhancing convenience without compromising security.
By prioritizing a user-centric design that is clear, efficient and incorporates robust security measures, businesses can cultivate a positive login experience that fosters trust and user satisfaction.
In conclusion, secure login processes are the first line of defense against unauthorized access. However, achieving robust security shouldn’t come at the expense of a user-friendly experience. By implementing a multi-layered approach and prioritizing user-centric design principles, businesses can create login experiences that are both secure and convenient.
Fortunately, numerous free resources are available to help small businesses strengthen their cybersecurity posture. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) offers a wealth of guidance on cybersecurity best practices, including resources specifically tailored for small businesses (https://www.nist.gov/cybersecurity). Remember, a secure and user-friendly login process fosters trust with your customers and lays the groundwork for a strong overall cybersecurity posture.
Categorized in:
Comments